I have installed WordPress, but the URLs are generated with the following format:
https://www.mydomain.com/?p=123
Q. How can I set friendly URLs?
A. Friendly URLs are intended to improve the usability and accessibility of a website or web service by being immediately and intuitively meaningful to non-expert users. WordPress allows you to configure 6 types of URLs:
Administration > Settings > Permalinks
and we get the following options.
Plain is the default mode and it’s the mode mentioned in the question.
Other formats work in a similar way so we will only explain the format of “Custom structure”, the /%category%/%postname%/ value means that the format would be:
https://www.mydomain.com/category/post-example/
A example of URL would be:
https://www.librebyte.net/cms/how-to-configure-friendly-urls-in-wordpress/
After you save the changes you must verify that the mod_rewrite module is loaded by the Apache, if you use Fedora, CentOS or RHEL you can run the following commands:
$ grep rewrite -R /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/
/etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf:LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.soFor any distribution, you can run
$ apachectl -M | grep -i rewrite
rewrite_module (shared)Verify you have a .htaccess file in the root directory of your project like:
# BEGIN WordPress
# If you uncomment IfModule directive you must set AllowOverride All
#
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
#
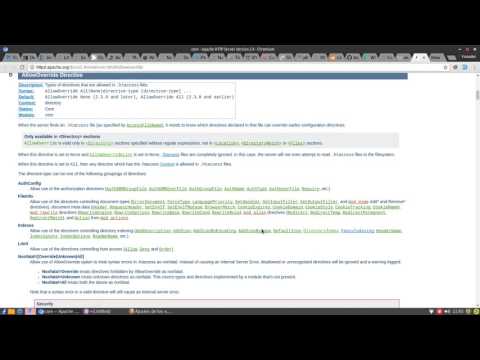
# END WordPressMost of the Hosting providers allow .htaccess files, if you’ve installed and configured WordPress on a dedicated server or a VPS then look in the web server main configuration (/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf for CentOS/Fedora/RHEL, /etc/apache2/apache2.conf for Debian/Ubuntu) the Directory directive that is pointing to the root directory of your project, Verify that AllowOverride and AllowOverrideList (this directive should be inside a Directory section) have the following values:
AllowOverride: must have All value or includes the FileInfo value, example:
AllowOverride FileInfo Limit
If AllowOverride has None value then the directive AllowOverrideList should have the following configuration
AllowOverrideList RewriteEngine RewriteOptions RewriteBase RewriteCond RewriteRule
If you did any changes to the previous directives then you should restart the Apache server
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd (Fedora/CentOS/RHEL) $sudo systemctl restart apache2 (Debian/Ubuntu)
For NGINX, use a similar configuration to:
# Upstream to abstract backend connection(s) for PHP
# php-fpm is the docker container name where the php-fpm service is running.
# The NGINX server is running inside a docker container too and it's linked to
# php-fpm docker container.
upstream fpm {
server php-fpm:9000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.librebyte.net;
root /var/www/html/librebyte;
index index.php;
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Add trailing slash to Wordpress Admin Panel requests, using
# full schema redirect due nginx is in a docker container with
# listen port = 80 and exposed port = 8080 (8080 -> 80)
rewrite /wp-admin$ $scheme://$http_host/wp-admin/ permanent;
location / {
# This is cool because no php is touched for static content.
# include the "?$args" part so non-default permalinks doesn't break when
# using query string
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include fastcgi.conf;
}
location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
}
FastCGI configuration file
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string; fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method; fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type; fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root; fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol; fastcgi_param REQUEST_SCHEME $scheme; fastcgi_param HTTPS $https if_not_empty; fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1; fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx/$nginx_version; fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr; fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr; fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name; # Mitigate https://httpoxy.org/ vulnerabilities fastcgi_param HTTP_PROXY ""; # PHP only, required if PHP was built with --enable-force-cgi-redirect fastcgi_param REDIRECT_STATUS 200; # Default file will be requested fastcgi_index index.php; # Linked to fpm upstream name fastcgi_pass fpm;
Recommended reading
Spanish Video associated with the Post